Strawberry cultivation is a delicate process with many key stages punctuated by the seasons. From winter dormancy to spring flowering, through summer fruiting and harvest, each phase requires specific care to ensure the optimal production of delicious strawberries. This article explores the complete cycle of the strawberry, highlighting the essential techniques and challenges encountered throughout the year.
Winter Dormancy
Like many species, strawberry plants enter dormancy during the winter period, which lasts from January to March. This rest phase is essential for their life cycle and future production. During this time, strawberries plants reduce their metabolic activity, resulting in partially dead leaves turned toward the ground. The plants appear almost inactive, but this phase is crucial for their regeneration.
There is no specific maintenance required during this dormancy period. However, it is important to ensure that the plants are protected against extreme winter conditions. For example, a mulch cover can be applied to protect the roots from frost.
Winter dormancy allows strawberry plants to rest and prepare for the next growing season.
The Spring Phase
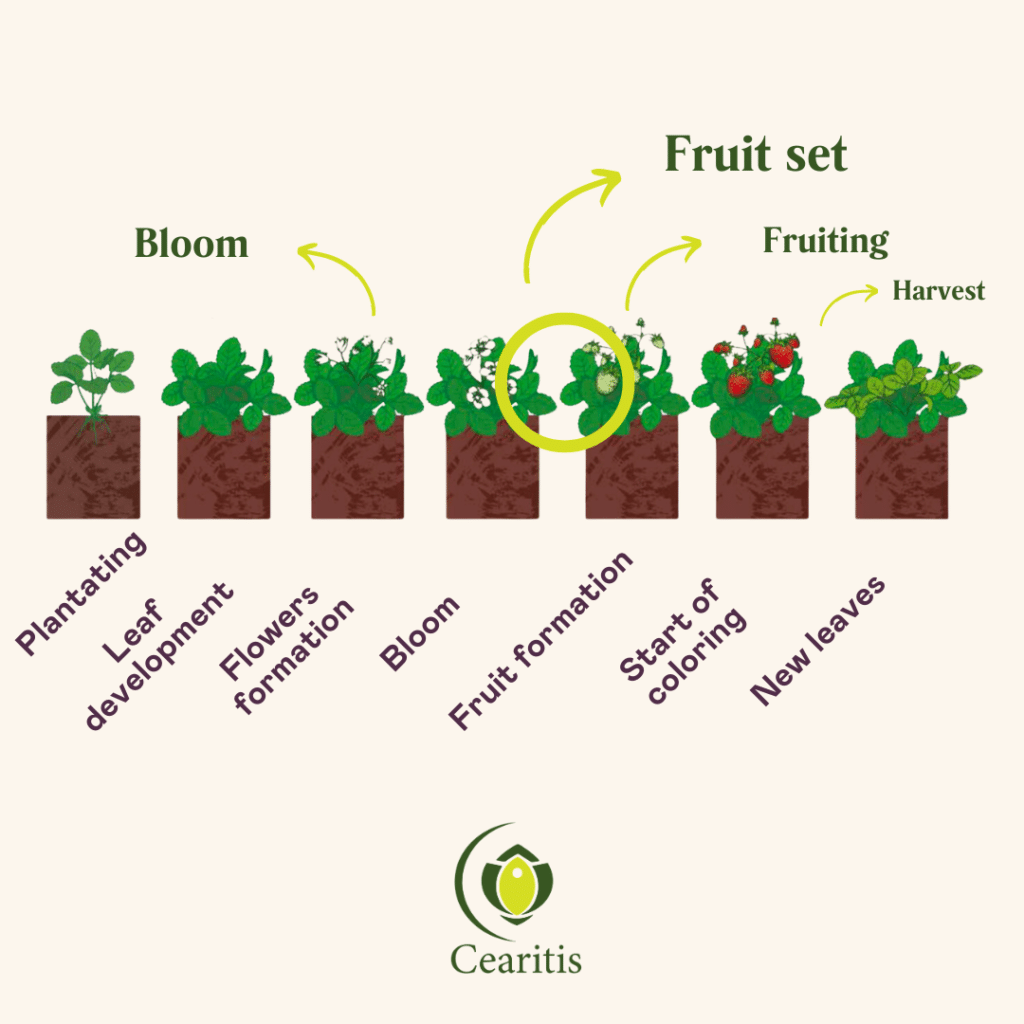
Temperatures are slowly rising and the days are getting longer: spring is here, and nature waking up. The first buds appear, gradually developing into vibrant flowers. This is the eagerly awaited time of blooming.
Strawberry blooming typically varies between February and September, depending on climatic conditions and the strawberry varieties cultivated. This marks the beginning of the strawberry plants’ reproductive cycle, where the flowers open to allow pollination.
Pollinators such as bees, hoverflies, and other insects get to work, facilitating the transformation of flowers into fruits. Pollination is a crucial step, as it allows fruit set, where fertilized flowers begin to turn into fruits. Optimal conditions of temperature, humidity, and nutrition are necessary for this transformation to proceed smoothly.
Pollination directly influences the size and shape of the fruits. Effective pollination, where a sufficient amount of pollen is transferred to the flowers, leads to better fertilization. This results in larger and more uniformly shaped fruits. Indeed, good fertilization promotes balanced fruit development.
Conversely, insufficient pollination can lead to deformed or small fruits. Therefore, the presence and intensive activity of numerous pollinators are crucial to ensure harvests that are not only abundant but also of high quality.
During this period, it is essential to monitor the condition of the plants and provide the necessary care, such as adequate irrigation.
The Summer Season
The long-awaited strawberry harvest generally extends from April/May to August. It is the culmination of many months of work and must be carried out meticulously to preserve the quality of the fruits. Ripe strawberries detach easily with a slight twist, and it is advisable to pick them in the morning to maintain their freshness. Once harvested, they should be sorted and cooled quickly to extend their shelf life. Managing climatic conditions and peak production periods is a challenge, but with sustainable practices and a well-trained workforce, it is possible to ensure an optimal and high-quality harvest.
The strawberry cycle, from winter dormancy to the summer harvest, is a complex process that requires constant attention and care tailored to each season. Every stage, whether it’s winter rest, spring flowering, fruiting, or harvesting, plays a crucial role in producing delicious and high-quality strawberries. By adopting sustainable and innovative practices, such as biocontrol, it is possible to overcome the challenges posed by pests and minimize environmental impact. Through a continuous commitment to quality and sustainability, we can ensure that each strawberry harvest is not only abundant but also environmentally friendly.